This Article has been revised, edited and added to, by Poulomi Chakraborty.
- Understanding ADA Compliance and SEO
- The Intersection of ADA Compliance and SEO
- Comparison: ADA Compliance vs. SEO Best Practices
- Practical Steps to Achieve ADA Compliance and Improve SEO
- The Business Benefits of ADA Compliance and SEO
- Tools and Resources for Achieving ADA Compliance and SEO
- Accessibility Testing Tools
- SEO Tools
- Online Resources
- Strategic Use of Accessibility Testing Tools
- Integrating SEO Tools for Comprehensive Analysis
- Advanced Techniques with ARIA Landmarks and Roles
- Enhancing User Experience with Descriptive Link Text
- Utilizing Color Contrast Analyzers for Design
- Implementing and Testing Accessible Forms
- Regular Updates and Continuous Learning
- Building a Cross-Functional Team
- Leveraging Analytics for Ongoing Improvement
- Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
- Future Trends: ADA Compliance and SEO
- Integrating ADA Compliance and SEO
- Conclusion
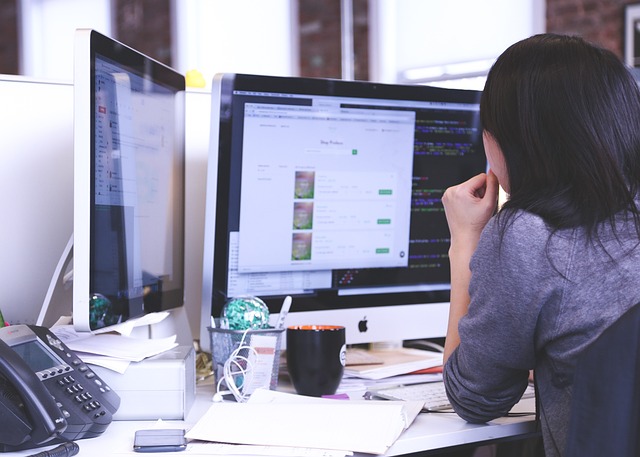
Navigating the digital world can be tricky, especially when you’re trying to meet both ADA compliance and SEO standards. But here’s the good news: achieving one often helps with the other. By ensuring your website is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, you are also enhancing your site’s SEO. This win-win situation not only broadens your audience but also improves your search engine rankings. Let’s dive into the details of how ADA compliance and SEO intersect and why it’s crucial for your website’s success.
Understanding ADA Compliance and SEO
What is ADA Compliance?
ADA, or the Americans with Disabilities Act, was established to ensure that people with disabilities have the same rights and opportunities as everyone else.
When it comes to websites, ADA compliance means that your digital content must be accessible to individuals with disabilities. This includes those who are blind, deaf, or have other impairments that affect their ability to use the internet.
What is SEO?
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the process of optimizing your website to rank higher on search engine results pages (SERPs). It involves various techniques and strategies to make your website more attractive to search engines, thereby increasing organic traffic.
How ADA Compliance Boosts SEO
At first glance, ADA compliance and SEO might seem like two separate goals. However, many elements that make a website accessible also enhance its SEO.
For instance, using alt text for images not only helps screen readers describe images to visually impaired users but also provides search engines with more information about your content. This dual benefit is one of the many ways ADA compliance can improve your SEO efforts.
The Intersection of ADA Compliance and SEO
Enhancing User Experience
One of the core principles of both ADA compliance and SEO is improving user experience. A website that is easy to navigate and understand will keep users engaged longer, reduce bounce rates, and increase conversions.
Accessible websites ensure that all users, regardless of their abilities, can interact with your content seamlessly. This inclusive approach not only fulfills legal requirements but also broadens your audience base.
Alt Text and Image Optimization
Alt text, or alternative text, is used to describe images on a webpage. For ADA compliance, alt text allows screen readers to convey the content of images to visually impaired users.
From an SEO perspective, alt text helps search engines understand the context of images, contributing to better rankings in image search results. By thoughtfully crafting descriptive alt text, you can achieve compliance and improve your SEO simultaneously.
Keyboard Navigation and Internal Linking
Many users with disabilities rely on keyboard navigation to move through a website. Ensuring your site is fully navigable via keyboard not only makes it accessible but also enhances its usability for all users.
Internal linking, a critical SEO practice, can be optimized for keyboard navigation. Clear, logical linking structures help both users and search engines understand the hierarchy and relationship of your content, boosting your SEO.
Video and Audio Content
Providing captions for videos and transcripts for audio content is another crucial aspect of ADA compliance. These features make your content accessible to deaf or hard-of-hearing users.
Moreover, transcripts provide additional text that search engines can index, thereby improving your SEO. Ensuring your multimedia content is accessible enhances user engagement and searchability.
Comparison: ADA Compliance vs. SEO Best Practices
Content Structure and Readability
Both ADA compliance and SEO emphasize the importance of well-structured, readable content. For ADA compliance, this means using clear headings, short paragraphs, and bulleted lists to break up text. Screen readers rely on these elements to help users navigate and understand the content.
SEO best practices also advocate for clear, structured content because it improves user experience and helps search engines index your pages more effectively. By focusing on readability, you can enhance accessibility and SEO simultaneously.
Mobile Accessibility and SEO
With the increasing use of mobile devices, ensuring your website is mobile-friendly is essential for both ADA compliance and SEO. Mobile accessibility involves creating a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes and touch interfaces, making it easier for users with disabilities to interact with your site on mobile devices.
From an SEO perspective, mobile-friendliness is a ranking factor, as search engines prioritize sites that offer a good user experience on mobile. By optimizing for mobile, you can improve both accessibility and SEO.
Speed and Performance
Website speed is a critical factor for user experience, ADA compliance, and SEO. Slow-loading pages can be frustrating for all users, particularly those with disabilities who may rely on assistive technologies that require fast and reliable access to content.
Search engines also consider page speed as a ranking factor. By optimizing your website’s performance, you can ensure a better experience for users and achieve higher search engine rankings.
Voice Search and Accessibility
Voice search is becoming increasingly popular, and it has significant implications for both ADA compliance and SEO. For users with disabilities, voice search offers a convenient way to interact with websites.
Optimizing your site for voice search involves using natural language and long-tail keywords, which can improve your site’s SEO. By considering voice search, you can make your website more accessible and boost its visibility in search results.
Practical Steps to Achieve ADA Compliance and Improve SEO
Conducting an Accessibility Audit
The first step towards ADA compliance and enhancing your SEO is to conduct a comprehensive accessibility audit of your website. This process involves evaluating your site against the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to identify areas that need improvement.
There are several tools available, such as WAVE and AXE, which can help you pinpoint accessibility issues. An audit will give you a clear understanding of what needs to be addressed to ensure your site is accessible to all users.
Implementing ARIA Landmarks and Roles
ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) landmarks and roles are essential for making web content more accessible. These elements help assistive technologies understand the structure and purpose of your web content, making it easier for users with disabilities to navigate your site.
For instance, using ARIA roles like “banner,” “navigation,” “main,” and “contentinfo” can enhance the browsing experience for users relying on screen readers. Implementing ARIA roles not only aids accessibility but also helps search engines better understand your site’s structure, thereby boosting SEO.
Using Descriptive Link Text
Descriptive link text is crucial for both ADA compliance and SEO. Instead of using generic phrases like “click here” or “read more,” use text that clearly describes the link’s destination. This practice helps users with disabilities understand the context of the link, enhancing their browsing experience.
For SEO, descriptive link text provides additional context to search engines about the content of the linked page, which can improve your site’s relevance and ranking.
Ensuring Color Contrast
Proper color contrast is vital for making text readable for users with visual impairments. The WCAG provides guidelines on minimum contrast ratios between text and background colors.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can ensure that your content is accessible to users with low vision. Additionally, high contrast text is easier for all users to read, improving overall user experience. This accessibility improvement can indirectly benefit your SEO, as search engines favor sites that offer a positive user experience.
Creating Accessible Forms
Forms are a critical part of many websites, whether for contact, registration, or purchasing purposes. Ensuring your forms are accessible involves several steps:
- Label Elements Clearly: Each form field should have a visible label or an ARIA label that screen readers can announce.
- Provide Instructions: Offer clear instructions and error messages that help users understand what is required.
- Keyboard Navigation: Ensure that users can navigate through the form using only the keyboard.
Accessible forms not only enhance usability for all users but also contribute to lower bounce rates and higher engagement, positively impacting your SEO.
Optimizing Multimedia Content
Multimedia content, such as videos and podcasts, can be made accessible by providing captions, transcripts, and audio descriptions. Captions and transcripts not only make your content accessible to users with hearing impairments but also provide additional text for search engines to index.
This practice enhances your content’s SEO by increasing its discoverability. Audio descriptions help visually impaired users understand the visual content of videos, further improving accessibility.
Improving Navigation and Sitemap
A clear, intuitive navigation structure is crucial for both ADA compliance and SEO. Ensure that your website’s navigation can be easily used with a keyboard and that all interactive elements are accessible. A well-organized sitemap helps search engines crawl your site more effectively, improving your SEO. It also aids users with disabilities in understanding the layout of your site, providing a better user experience.
Regular Testing and Updates
Achieving ADA compliance and maintaining high SEO standards is an ongoing process. Regularly testing your website for accessibility issues and SEO performance is essential.
Use automated tools to perform regular audits and engage with users with disabilities to gather feedback on your site’s accessibility. Continuously update your content and design to meet evolving guidelines and best practices. Staying proactive ensures that your website remains compliant and optimized for search engines.
The Business Benefits of ADA Compliance and SEO
Expanding Your Audience
By making your website accessible, you open it up to a larger audience, including the millions of people with disabilities. This inclusivity can lead to increased traffic, engagement, and potential customers. From an SEO perspective, a broader audience translates to more visits, higher engagement metrics, and ultimately, better search engine rankings.
Enhancing Brand Reputation
Companies that prioritize accessibility demonstrate a commitment to inclusivity and social responsibility. This positive perception can enhance your brand’s reputation, fostering loyalty and trust among your audience. A strong, positive brand image can lead to increased organic traffic as more users are likely to engage with and recommend your site.
Reducing Legal Risks
Non-compliance with ADA regulations can result in legal consequences, including lawsuits and fines. By ensuring your website meets accessibility standards, you mitigate the risk of legal issues.
Furthermore, an accessible site that also ranks well in search engines can provide a competitive edge, attracting more users and reducing the likelihood of legal challenges.
Improving User Engagement and Conversions
Accessible websites offer a better user experience for all visitors, not just those with disabilities. This improved experience can lead to longer site visits, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates.
From an SEO perspective, these positive user signals can boost your site’s rankings. By focusing on accessibility, you create a more engaging environment that encourages users to take desired actions, such as making a purchase or filling out a form.
Maximizing SEO Efforts
Many SEO techniques overlap with ADA compliance requirements. By optimizing your site for accessibility, you simultaneously enhance its SEO. This dual approach maximizes your efforts, ensuring that your website is both user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
The result is a site that performs well in search rankings while providing an inclusive experience for all users.

Tools and Resources for Achieving ADA Compliance and SEO
Accessibility Testing Tools
There are several tools available to help you test and improve your website’s accessibility:
- WAVE: A web accessibility evaluation tool that provides visual feedback on the accessibility of your web content.
- AXE: A browser extension that helps developers identify and fix accessibility issues.
- Lighthouse: An open-source tool from Google that audits performance, accessibility, and SEO.
Using these tools regularly can help you maintain ADA compliance and improve your site’s SEO.
SEO Tools
In addition to accessibility tools, there are SEO tools that can help you optimize your site:
- Google Search Console: Provides insights into your website’s search traffic and performance.
- Ahrefs: An SEO tool that offers keyword research, backlink analysis, and site audits.
- Moz: Provides SEO analytics, keyword research, and site crawl reports.
Integrating these tools into your workflow can help you monitor and enhance both your accessibility and SEO efforts.
Online Resources
Several online resources offer guidance on achieving ADA compliance and optimizing for SEO:
- W3C Web Accessibility Initiative (WAI): Provides comprehensive guidelines and resources for web accessibility.
- Moz Blog: Offers tips and strategies for improving your site’s SEO.
- Google Webmasters: Provides best practices for optimizing your website for search engines.
Strategic Use of Accessibility Testing Tools
For startup founders, leveraging accessibility testing tools is crucial for identifying and resolving issues efficiently. Begin by incorporating WAVE, AXE, and Lighthouse into your development workflow. These tools can help detect potential accessibility barriers and provide actionable insights.
Regularly run these tools during the development process to catch and fix issues early. This proactive approach saves time and resources in the long run and ensures your website is compliant from the outset.
Integrating SEO Tools for Comprehensive Analysis
SEO tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, and Moz are invaluable for optimizing your website’s performance. Start by using Google Search Console to monitor your website’s search traffic and identify any issues. Ahrefs and Moz can assist with in-depth keyword research, backlink analysis, and competitive analysis.
By integrating these tools, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your site’s SEO health and pinpoint areas for improvement. Combining this data with accessibility insights ensures your site is not only compliant but also optimized for search engines.
Advanced Techniques with ARIA Landmarks and Roles
ARIA landmarks and roles are essential for making dynamic web content accessible. For startup founders, it’s important to understand how to implement these elements strategically.
Use ARIA landmarks to define regions of your webpage, such as banners, navigation, and main content areas. These landmarks help assistive technologies navigate your site more effectively.
Additionally, assign ARIA roles to interactive elements to clarify their function. For example, using roles like “button,” “dialog,” or “alert” can enhance the user experience for individuals relying on screen readers. This strategic implementation not only improves accessibility but also aids in better content indexing by search engines.
Enhancing User Experience with Descriptive Link Text
Descriptive link text is a small but powerful tool for enhancing both accessibility and SEO. When creating content, ensure that link text clearly describes the destination or action. Avoid vague phrases like “click here” and instead use specific descriptions such as “read our latest blog post on SEO strategies.”
This practice improves navigation for users with disabilities and provides search engines with contextual information, boosting your SEO. Incorporating descriptive link text consistently across your site can lead to a more intuitive and search-friendly environment.
Utilizing Color Contrast Analyzers for Design
Proper color contrast is vital for readability and accessibility. Use tools like the WebAIM Contrast Checker to ensure your text stands out against background colors. For startup founders, it’s essential to incorporate these checks into your design process.
High contrast improves readability for users with visual impairments and enhances the overall user experience. This focus on visual accessibility can indirectly benefit your SEO, as search engines favor sites with positive user engagement metrics.
Implementing and Testing Accessible Forms
Forms are critical for user interaction, whether for sign-ups, feedback, or purchases. To ensure your forms are accessible, label elements clearly and provide helpful instructions. Use tools like WAVE or AXE to test form accessibility and identify any issues.
For startup founders, integrating accessible form practices from the beginning can prevent costly redesigns and ensure all users can interact with your site effectively. Accessible forms reduce user frustration, leading to higher completion rates and improved conversion metrics, which positively impact SEO.
Regular Updates and Continuous Learning
Staying compliant and optimized requires ongoing effort. Subscribe to updates from the W3C Web Accessibility Initiative and SEO resources like Moz Blog and Google Webmasters. Attend webinars and workshops to stay informed about the latest trends and best practices.
For startup founders, fostering a culture of continuous learning within your team ensures that your website remains up-to-date with both accessibility and SEO standards. Regularly revisiting and updating your site in response to new guidelines and user feedback keeps your site relevant and compliant.
Building a Cross-Functional Team
Achieving ADA compliance and SEO excellence requires a collaborative approach. Assemble a cross-functional team that includes designers, developers, content creators, and SEO specialists. Encourage regular communication and collaboration to ensure accessibility and SEO considerations are integrated into every stage of development.
For startup founders, this team approach ensures that all aspects of your website are aligned with best practices, leading to a more cohesive and effective online presence.
Leveraging Analytics for Ongoing Improvement
Use analytics tools to track the performance of your accessibility and SEO efforts. Google Analytics can provide insights into user behavior, helping you understand how users interact with your site. Look for metrics such as bounce rates, session duration, and conversion rates to gauge the effectiveness of your improvements.
For startup founders, using this data to make informed decisions can lead to continuous enhancements in both accessibility and SEO, driving sustained growth and success.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them

Balancing Design and Accessibility
One common challenge is balancing aesthetic design with accessibility requirements. While it’s important to have a visually appealing website, accessibility should never be compromised. To achieve this balance, collaborate with designers who understand both design principles and accessibility standards.
Use color contrast tools to ensure text is readable and design elements are accessible. Remember, an accessible design can still be beautiful and engaging.
Staying Updated with Guidelines
The guidelines for both ADA compliance and SEO are constantly evolving. Staying updated can be challenging but is crucial for maintaining compliance and optimizing your site.
Subscribe to newsletters from reputable sources like W3C, Google Webmasters, and leading SEO blogs. Attend webinars and workshops to stay informed about the latest changes and best practices. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to staying ahead.
Ensuring Consistent Implementation
Implementing accessibility and SEO best practices consistently across your website can be difficult, especially for large sites with multiple contributors. Establish clear guidelines and standards for your team to follow.
Conduct regular audits and provide training to ensure everyone is aware of and adheres to these standards. Consistent implementation ensures that your site remains accessible and optimized at all times.
Handling Legacy Content
Updating legacy content to meet current accessibility and SEO standards can be daunting. Prioritize the most important pages, such as those with the highest traffic or critical information. Use automated tools to identify and fix issues quickly.
Gradually update remaining content as resources allow. By taking a phased approach, you can manage the workload more effectively while making steady progress towards full compliance and optimization.
Future Trends: ADA Compliance and SEO

Voice Search and Accessibility
Voice search technology is rapidly growing in popularity, and it’s changing how users interact with websites. This trend has significant implications for both ADA compliance and SEO. Users with disabilities, particularly those with visual impairments, often rely on voice search to navigate the internet.
Optimizing your website for voice search involves using natural language and long-tail keywords, which aligns with SEO best practices. By focusing on voice search optimization, you can enhance accessibility and improve your site’s search engine rankings.
AI and Machine Learning in Accessibility
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming how we approach web accessibility. AI-powered tools can automatically generate alt text for images, identify accessibility issues, and suggest improvements. For instance, platforms like Microsoft’s Seeing AI use AI to describe surroundings for visually impaired users.
Integrating AI and ML into your accessibility strategy can streamline the process of achieving ADA compliance and maintaining SEO standards. These technologies are evolving rapidly, offering new opportunities to enhance both accessibility and SEO.
Personalized User Experiences
Personalization is becoming increasingly important in digital marketing. For ADA compliance, personalization can mean tailoring content to meet the specific needs of users with disabilities. For example, providing adjustable text sizes, customizable color schemes, and voice-assisted navigation can create a more inclusive experience.
From an SEO perspective, personalized content can improve user engagement and satisfaction, leading to higher search rankings. Embracing personalization as part of your accessibility and SEO strategy can help you meet diverse user needs and enhance your site’s performance.
Mobile Accessibility Advancements
As mobile device usage continues to rise, ensuring your website is accessible on mobile platforms is crucial. Future trends indicate a growing emphasis on mobile-first design, which prioritizes mobile accessibility from the start.
Techniques like responsive design, touch-friendly navigation, and simplified layouts can make your site more accessible on mobile devices.
Mobile accessibility not only meets ADA requirements but also aligns with Google’s mobile-first indexing, which favors mobile-friendly sites in search rankings. By staying ahead of mobile accessibility trends, you can improve both user experience and SEO.
Legislation and Regulatory Changes
The landscape of digital accessibility is shaped by evolving legislation and regulations. Staying informed about changes in laws and guidelines, such as updates to the ADA or new international standards, is essential. Anticipating these changes and proactively adapting your website can help you maintain compliance and avoid legal risks.
Additionally, demonstrating a commitment to accessibility can enhance your brand reputation and attract a broader audience. Monitoring regulatory trends ensures that your site remains compliant and competitive in the evolving digital landscape.
Integrating ADA Compliance and SEO
Achieving ADA compliance and optimizing for SEO should not be viewed as separate tasks but rather as complementary goals that enhance each other. By making your website accessible, you improve the user experience for all visitors, which in turn can boost your search engine rankings.
Both accessibility and SEO prioritize user-centered design, clear content structure, and high-quality user experiences. By integrating these principles, you create a website that is inclusive, user-friendly, and highly visible in search results.
The Long-Term Benefits
Investing in ADA compliance and SEO has long-term benefits for your business. An accessible website can attract a broader audience, including millions of users with disabilities. This inclusivity can lead to increased traffic, engagement, and conversions.
From a legal perspective, ADA compliance helps you avoid lawsuits and fines, protecting your business from potential legal issues. Additionally, a site that ranks well in search results can drive sustained organic traffic, reducing your reliance on paid advertising. The combined focus on accessibility and SEO creates a solid foundation for long-term success.
Taking Action
To achieve ADA compliance and optimize your SEO, start by conducting a thorough audit of your website. Identify areas that need improvement and implement best practices for accessibility and SEO. Use the tools and resources available to guide your efforts and stay updated with the latest trends and regulations.
Regular testing and updates are essential to maintaining compliance and optimizing performance. By taking proactive steps, you can create a website that serves all users effectively and stands out in search engine rankings.
A Call to Inclusivity
Building an accessible website is not just about meeting legal requirements or improving SEO. It’s about creating an inclusive digital space where everyone, regardless of their abilities, can access and enjoy your content. By prioritizing ADA compliance, you demonstrate a commitment to social responsibility and inclusivity.
This commitment can enhance your brand reputation, foster customer loyalty, and contribute to a more equitable digital world. Embrace the principles of accessibility and SEO to build a website that truly serves all users and achieves sustainable success.
Conclusion
Integrating ADA compliance and SEO is a strategic move that enhances both user experience and search engine performance. By making your website accessible, you cater to a broader audience, including millions of users with disabilities, and improve your site’s usability for all visitors. This dual focus leads to increased traffic, engagement, and conversions, while also protecting your business from legal risks associated with non-compliance.
Investing in accessibility is not just about meeting legal requirements; it’s about creating an inclusive digital environment that reflects your commitment to social responsibility. This inclusivity builds a stronger brand reputation and fosters customer loyalty. Stay proactive by conducting regular audits, staying updated with guidelines, and continuously improving your website. By doing so, you ensure that your website remains a valuable, accessible, and high-performing asset in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
READ NEXT:



















